China Dominates Global Silicon Production for Solar Energy, Transforming Solar Panel Economics
Alayaran.com - The global landscape of solar photovoltaic energy has been dramatically reshaped by the dominance of China in the production of high-purity silicon, the critical raw material for solar panels. As of 2023, Chinese firms control 93% of the world's silicon supply for solar cells, a strategic position bolstered by government support and substantial investments in manufacturing capabilities.
From Sand to Silicon
The journey of silicon begins with quartz-rich sand, which is heated to 1,900°C in electric arc furnaces along with carbon, primarily in the form of coke. This process results in the creation of molten polysilicon through the reaction:
SiO2 + C → Si + CO2
The silicon is then purified through a series of chemical reactions involving hydrochloric acid, culminating in the production of ultra-pure silicon known as "electronic grade," which is 99.99999999% pure. This high level of purity was once exclusively demanded by the semiconductor industry for microchips, but the surge in demand for solar energy has shifted dynamics.
Geopolitical Dynamics and Economic Impacts
Initially, the solar industry utilized the silicon waste from the semiconductor sector. However, with government subsidies fueling demand for solar energy, new factories dedicated solely to photovoltaic silicon production emerged, predominantly in Asia, with China leading the charge. Today, companies like GCL-Poly and Tongwei have production capacities that not only meet but exceed global demand. Tongwei, for instance, is investing $4 billion in a new plant aimed at producing 400,000 tons annually.
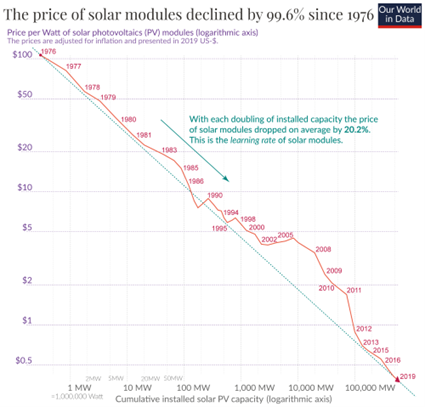
This dominance has profound economic implications. The competitive landscape in China's silicon production has led to relentless cost-cutting and technological advancements, driving down the prices of solar panels. From the 1970s to 2020, the cost of solar panels has plummeted by a factor of 500, from roughly €100 per watt to €0.2 per watt, following a steep learning curve where costs decrease by 21% with every doubling of installed capacity.
Modularity and Market Penetration
Solar photovoltaic technology's modularity allows it to cater to a diverse range of consumers, from individuals installing small-scale systems to large corporations developing gigawatt-scale solar farms. This unique attribute has not only democratized access to renewable energy but also fostered an environment of intense innovation and competition.
Social and Environmental Considerations
Despite some resistance to large-scale solar farms due to their visual impact, solar panels generally enjoy a high level of public acceptance, or "social license," compared to other forms of energy generation. This acceptance is partly due to the technology's scalability and the relatively lower environmental footprint compared to alternatives like nuclear or fossil fuels.
As Professor Ignacio Mártil of the Complutense University of Madrid notes, "The solar industry's evolution is just beginning. The relentless decrease in costs and the technological advancements promise a future where solar energy could become the cornerstone of global energy systems."
This transformation in the solar industry underscores a pivotal shift in energy production, with significant implications for global energy markets, environmental policies, and geopolitical strategies centered around renewable resources.
