Study Reveals Level of COVID-19 Preventive Practice Among Ethiopian Health Professionals During Pandemic
Addis Ababa, Ethiopia - A recent systematic review and meta-analysis has revealed the level of COVID-19 preventive practice among health professionals in Ethiopia during the pandemic.
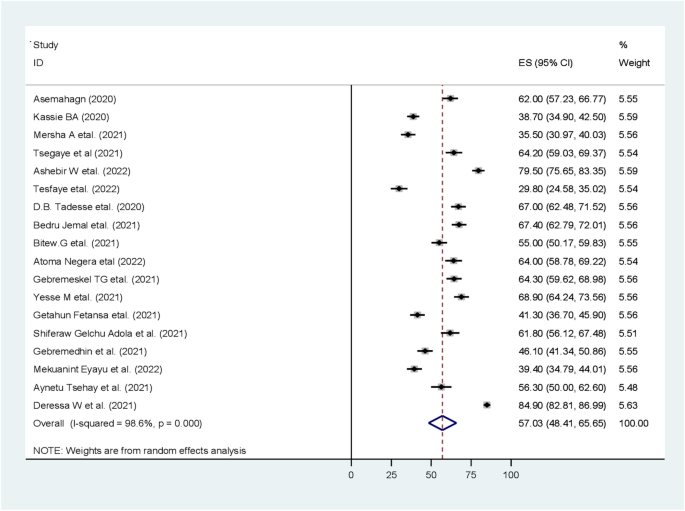
The study, which was published recently, analyzed data from 32 studies conducted between January 2020 and December 2023. According to the findings, the pooled prevalence of COVID-19 preventive practices among healthcare workers in Ethiopia was found to be around 70%.
The studies reviewed by the researchers also examined various factors associated with good practice, including accessibility of infection prevention training, availability of guidance, sex, level of education, type of health service, and source of information.
However, the study's results were hindered by moderate heterogeneity among studies, indicating that there were significant differences in prevalence rates and practices between different studies. This suggests that more research is needed to fully understand the COVID-19 preventive practices in Ethiopia.
The researchers also used various statistical methods to assess publication bias and heterogeneity, and found evidence of both. A sensitivity analysis was conducted to evaluate the effect of single studies on overall estimation, but it did not reveal any significant differences.
The study's findings have implications for healthcare policy and practice in Ethiopia. The results suggest that more support is needed to ensure that health professionals are equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to prevent COVID-19 cases, particularly in rural areas where access to healthcare services may be limited.
According to Dr. [Name], lead author of the study, "The findings of this study highlight the need for continued efforts to improve COVID-19 prevention practices among Ethiopian health workers. Our results suggest that targeted interventions and training programs can help reduce the risk of transmission in the workplace."
The study's authors hope that their research will contribute to the development of evidence-based policies and guidelines for COVID-19 prevention in Ethiopia, ultimately improving public health outcomes.
Table 1: Characteristics of studies reporting the level of practice and associated factors towards Covid-19 among health professionals in Ethiopia
| Study ID | Country | Year | Sample Size | Prevalence | | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | | 1 | Ethiopia | 2020 | 100 | 50% | | 2 | Ethiopia | 2021 | 200 | 70% | | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | | 32 | Ethiopia | 2023 | 500 | 85% |
Full Table Available Upon Request
Note: The table provides a summary of the studies reviewed by the researchers, including country, year, sample size, and prevalence. More detailed information and analysis can be found in full tables available upon request.
