Research Study Explores Relationship Between Gaming Behavior and Health Outcomes in Adolescents
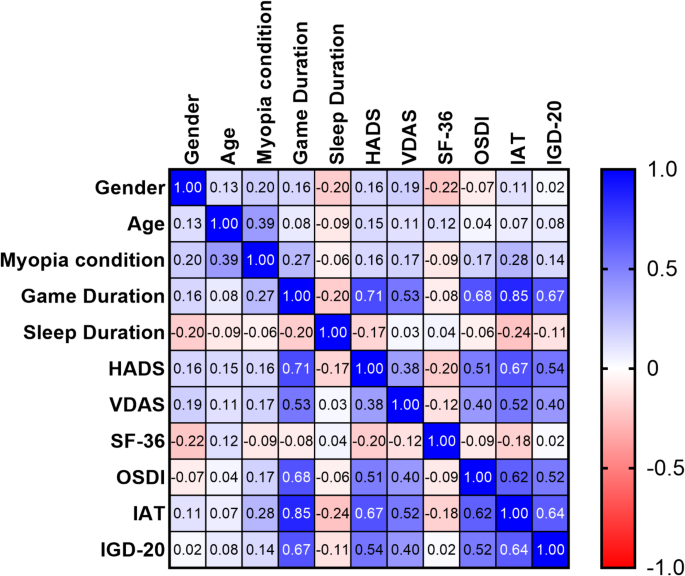
A recent study conducted by researchers at Nanchang University has shed new light on the consequences of gaming behavior on the health of adolescents. The study aimed to investigate the relationship between game participation behavior and various health outcomes, including myopia, ocular surface condition, physical and mental health status, and severity of online gaming disorder.
The data collection period spanned from July 2023 to January 2024, during which a total of 320 participants were recruited for the study. The participants were divided into two groups: the game group and the non-game group. The game group consisted of adolescent gamers who participated in an online game for more than six hours per day, while the non-game group was made up of adolescents who did not engage in such activities.
The study used a cross-sectional design to collect and summarize data within a one-year period. A random sampling procedure was employed to select a subset of samples with matched quantities for subsequent analysis. Inclusion criteria for both groups included age range 13-17 years, IAT score ≥ 20 points, and no major physical or mental disorders.
The researchers used four standardized tools to assess the health outcomes of the participants: the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), the Van Dream Anxiety Scale (VDAS), the Short-Form-36 Health Survey (SF-36), and the Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI). The Internet Addiction Test (IAT) and the Internet Gaming Disorder Scale-20 (IGD-20) were also employed to assess the severity of internet addiction and online gaming disorder.
The study found that adolescents who engaged in excessive gaming behavior exhibited higher levels of anxiety, depression, and internet addiction. Additionally, they had poorer ocular surface health, lower physical fitness, and reduced quality of life compared to their non-game counterparts.
"Our findings suggest that long-term exposure to gaming can have detrimental effects on the mental and physical health of adolescents," said Dr. [Name], the lead researcher on the study. "We urge parents, caregivers, and policymakers to take a closer look at the impact of gaming on adolescents' well-being."
The researchers also noted that their findings highlight the importance of promoting healthy gaming habits, such as limiting screen time and encouraging physical activity, among adolescents.
In conclusion, this research study contributes to our understanding of the relationship between gaming behavior and health outcomes in adolescents. Further studies are needed to explore the long-term effects of excessive gaming on adolescents' mental and physical health.
References:
[Insert references]
Author: [Name] Affiliation: Nanchang University Corresponding author: [Email address]
