Competences necessary for effective school sports coaching, with a focus on building strong relationships between coaches and athletes
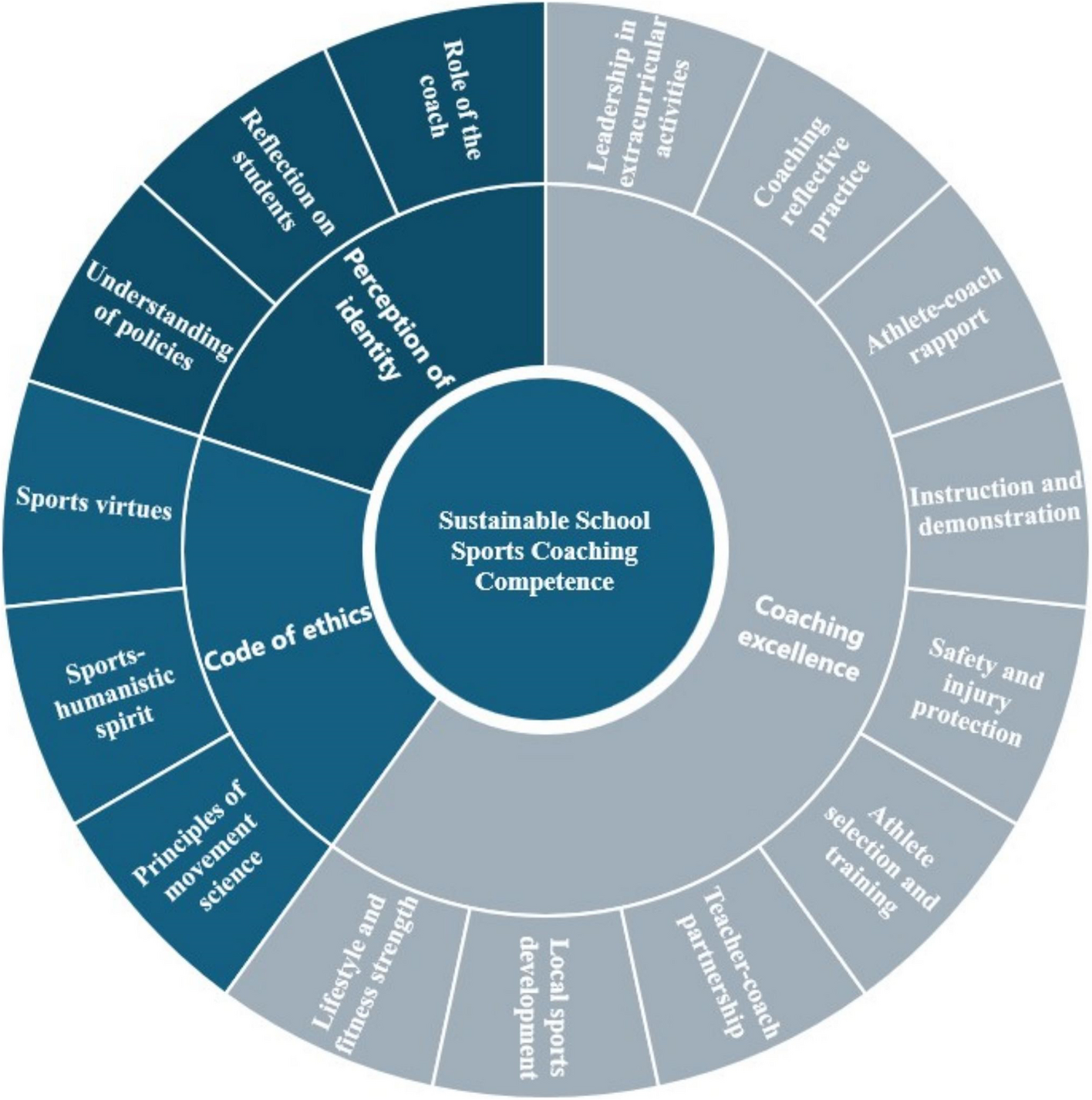
The provided text outlines the competences necessary for effective school sports coaching, with a focus on building strong relationships between coaches and athletes. The seven competencies described are:
Instruction and demonstration: This involves mastering the theoretical model of sports training, planning, implementing plans, assessing, making adjustments, and leading by example through reflective practice.
Decision-making skills for planning: School coaches need to tailor their training programs to the specific needs of students and take into account factors such as academic schedules to ensure that students achieve success both in school and sports.
Reflection and coaching improvement: This involves engaging in ongoing professional development, staying up-to-date on current best practices, being open to learning from colleagues, continuing with self-assessment through feedback, and leveraging technology for training purposes.
The ability to build strong relationships: Coaches should be skilled at making inclusive decisions through tactics, fostering collaborative environments within teams, establishing effective resource distribution, and creating policies that guide sports competition operations.
Athlete-coach rapport building: Effective communication with team members is a critical aspect of school sports coaching as it involves setting goals for the team, using individualized techniques to foster stronger bonds between the coach and athletes, coordinating resources efficiently, and establishing clear regulations for sports training and competitions.
Coaching reflective practice (self-reflection): The process includes recognizing areas for improvement in order to make necessary adjustments that help a better-coaching performance over time.
Lifelong learning: This requires engaging in professional development, staying informed on updates in the area, continuing with ongoing self-assessment through personal reflection, and seeking support whenever required.
